Net Metering in a Solar Energy System & all You Need to Know About its Benefits to the Domestic and Corporate Consumer
4PEL Staff
December 2023
What is Net Metering?
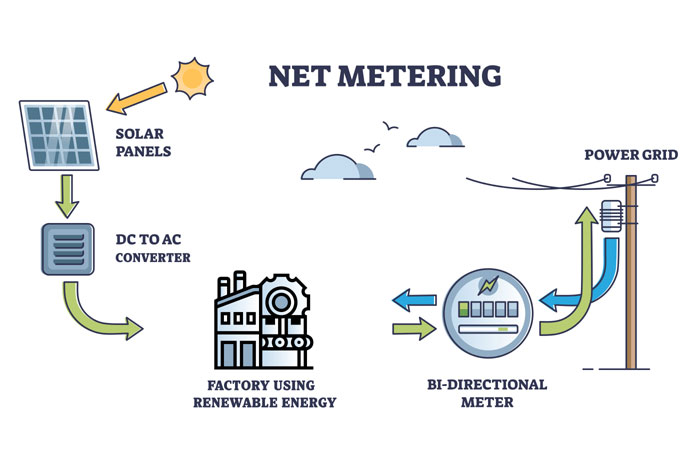
It is a simple billing arrangement that allows consumers of clean energy to connect their renewable energy systems i.e. solar panels to the grid. It enables them to offset their electricity consumption by generating excess power and feeding it back to the grid. Bidirectional meters are used to record both the energy consumed and the surplus energy exported to the grid.
It is a process where an individual or company can send back excess energy produced to the grid, in exchange for a financial or unit-based settlement – because this policy is used as a credit tool against the excess energy. It becomes extremely beneficial especially during nights and exceptionally cloudy days – where the consumer can draw electricity from the grid without incurring additional costs, using the credits gained. Alternatively, one can get paid for the excess electricity sent back to the grid, in accordance with units of power sent.
In India, each State has different regulations for the type of net meter used to record the power and the total capacity that can be offset.
Key Benefits of Net Metering
- Helps lower peak load demand conditions during the day and reduces load shedding –thereby helping Discoms reduce their T&C wheeling losses.
- In this process, the grid acts as a battery bank and ‘stores’ the excessive solar power generated for consumption during lean times, thereby eliminating the need for an expensive Diesel Generator
- Cost Savings: Net metering allows individuals and businesses to offset their electricity costs by earning credits for the excess energy they generate, resulting in significant savings on energy bills over time.
- If the amount of energy generated by the owner’s system is more than the amount of energy consumed, then the owner will receive extra credits and revenue.
Cap on Net Metering Capacities across States
Net Metering policies like most other tenets of power regulation, are often revised by State nodal agencies. States have set varied limits to cap the electricity that can be sent back to the grid by a single consumer/entity.
- Maharashtra – 5MW
- Telangana – 1MW
- Tamil Nadu – 1MW
- Gujarat – 1MW
India’s Net Metering Scenario and key Challenges
Net Metering has found favour in countries across the globe, that are prioritising energy transition. In India, while it is certainly gaining traction – there still exists several barriers that hinder widespread adoption.
The most confusing aspect of Net Metering in India is the lack of uniformity across States in its implementation. With India eyeing Net Zero by 2070, many States have adopted progressive Net Metering policies while others continue to impose restrictions. Some States are also introducing grid support charges on NM installations – while it is important to ensure the financial health of Discoms, excessive infrastructure charges may deter the consumer from adopting rooftop solar by shrinking the economic benefits of clean energy. systems A stable, long-term policy across the country will encourage domestic and commercial users to embrace renewables more aggressively.
Paving the Road for a cleaner, greener India
To achieve its 2030 renewable energy and 2070 Net Zero targets, India must look at implementation of a uniform, long-term clean energy policy framework – which balances the interests of Discoms, utilities, developers and consumers. Progressive policies will not only help accelerate decarbonization across the region, but it will also help attract the right kind of impact investment needed to implement this energy transition.


